Table of contents
Amazon DynamoDB is AWS's offering of a fast, scalable, and fully-managed NoSQL database. In DynamoDB you can define data types for your different attributes.
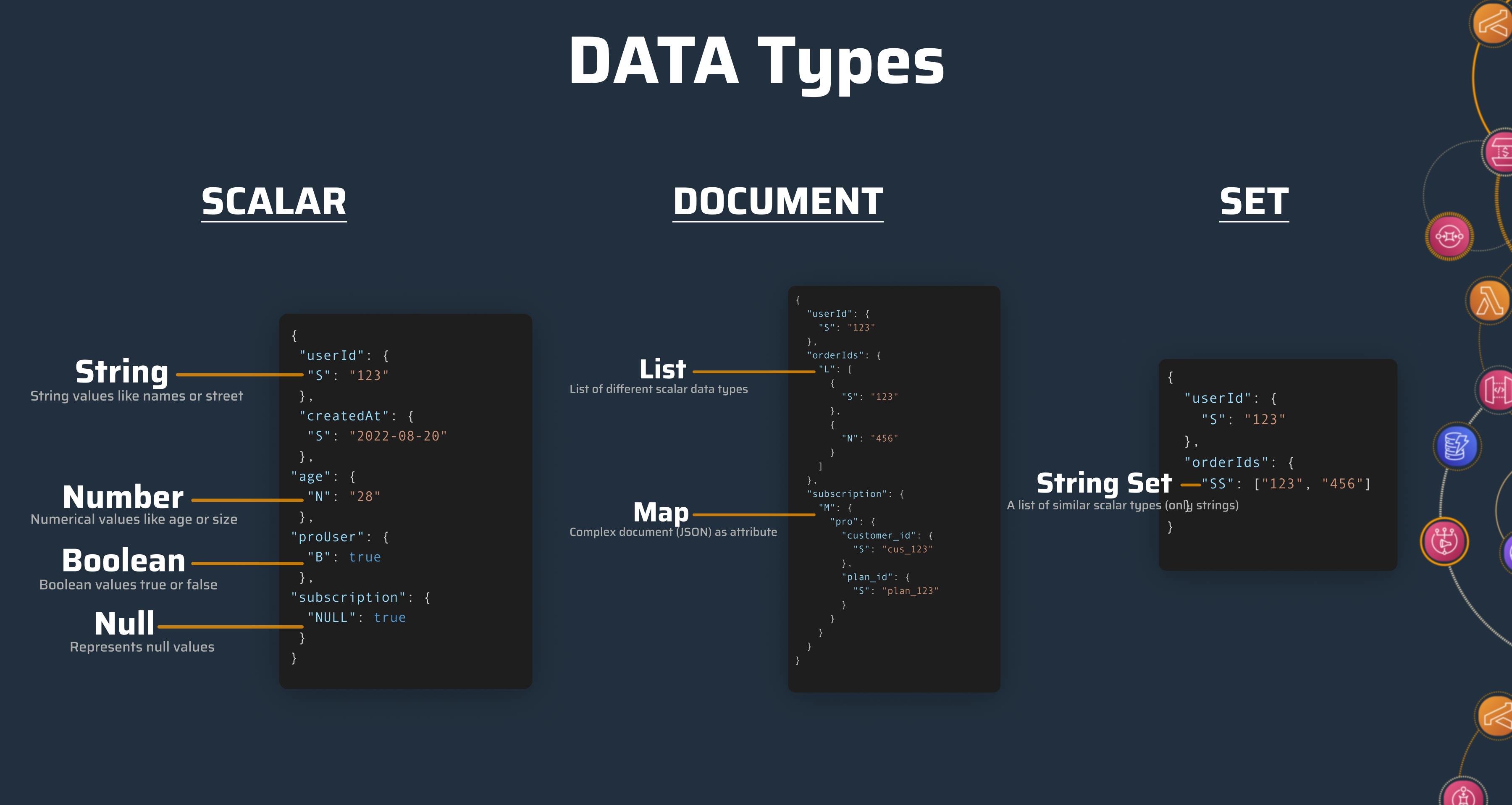
The data types can be separated into three different categories:
Scalar
Document
Set
Scalar Types
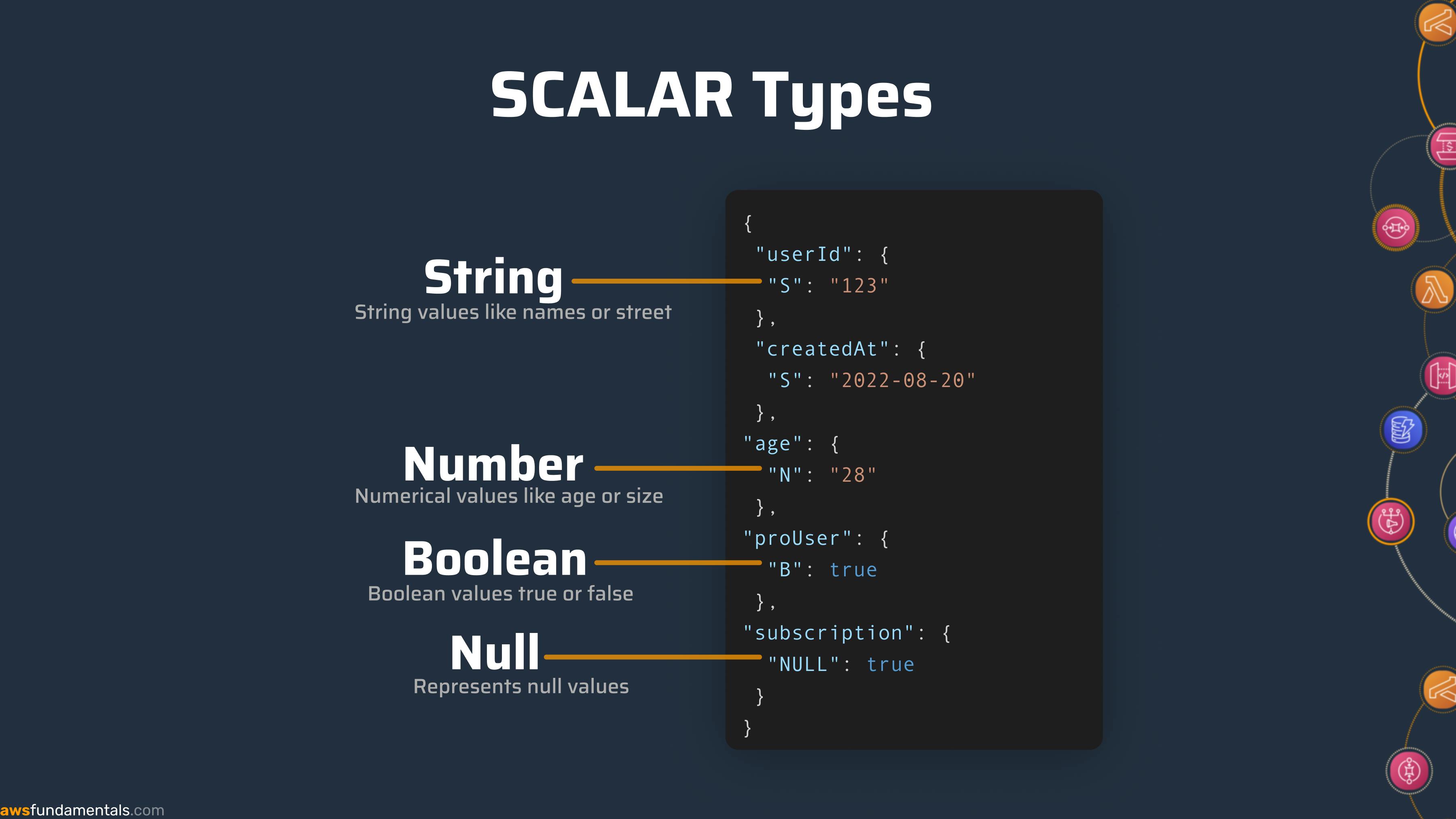
Scalar data types represent exactly one value. They are:
| Data type | DynamoDB Representation |
| String | S |
| Number | N |
| Binary | B |
| Boolean | BOOL |
| Null | NULL |
The DynamoDB JSON representation shows you how the datatypes are represented internally in DynamoDB. The normalized JSON view shows how you would work with the data in applications.
Take the following user table as an example:
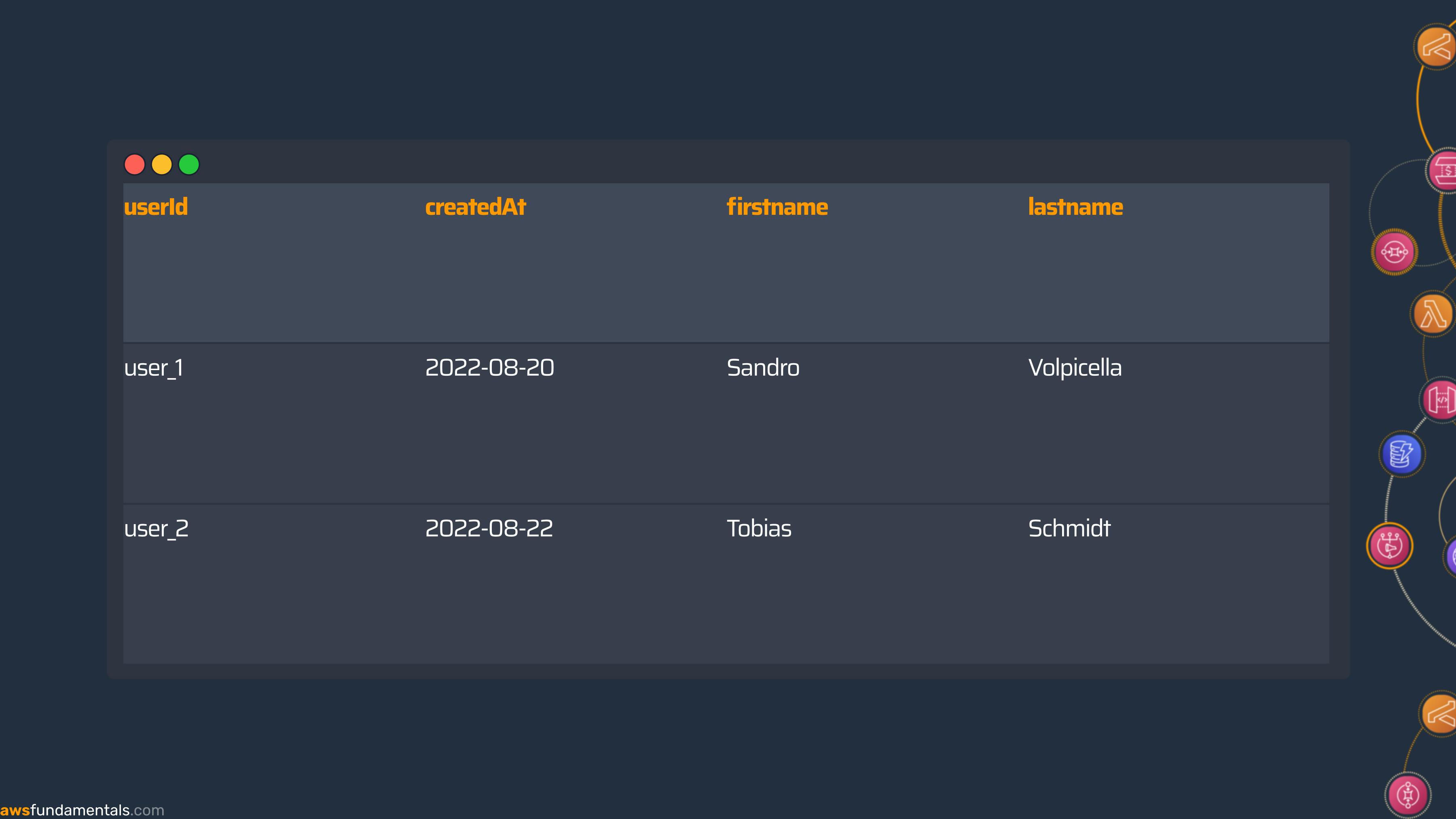
You can see the userId is a string (S) while age is a number (N).
DynamoDB JSON
{
"userId": {
"S": "123"
},
"age": {
"N": "28"
},
"createdAt": {
"S": "2022-08-20"
},
"firstname": {
"S": "Sandro"
},
"lastname": {
"S": "Volpicella"
}
}
Normalized JSON
{
"userId": "123",
"age": 28,
"createdAt": "2022-08-20",
"firstname": "Sandro",
"lastname": "Volpicella",
}
Document Types
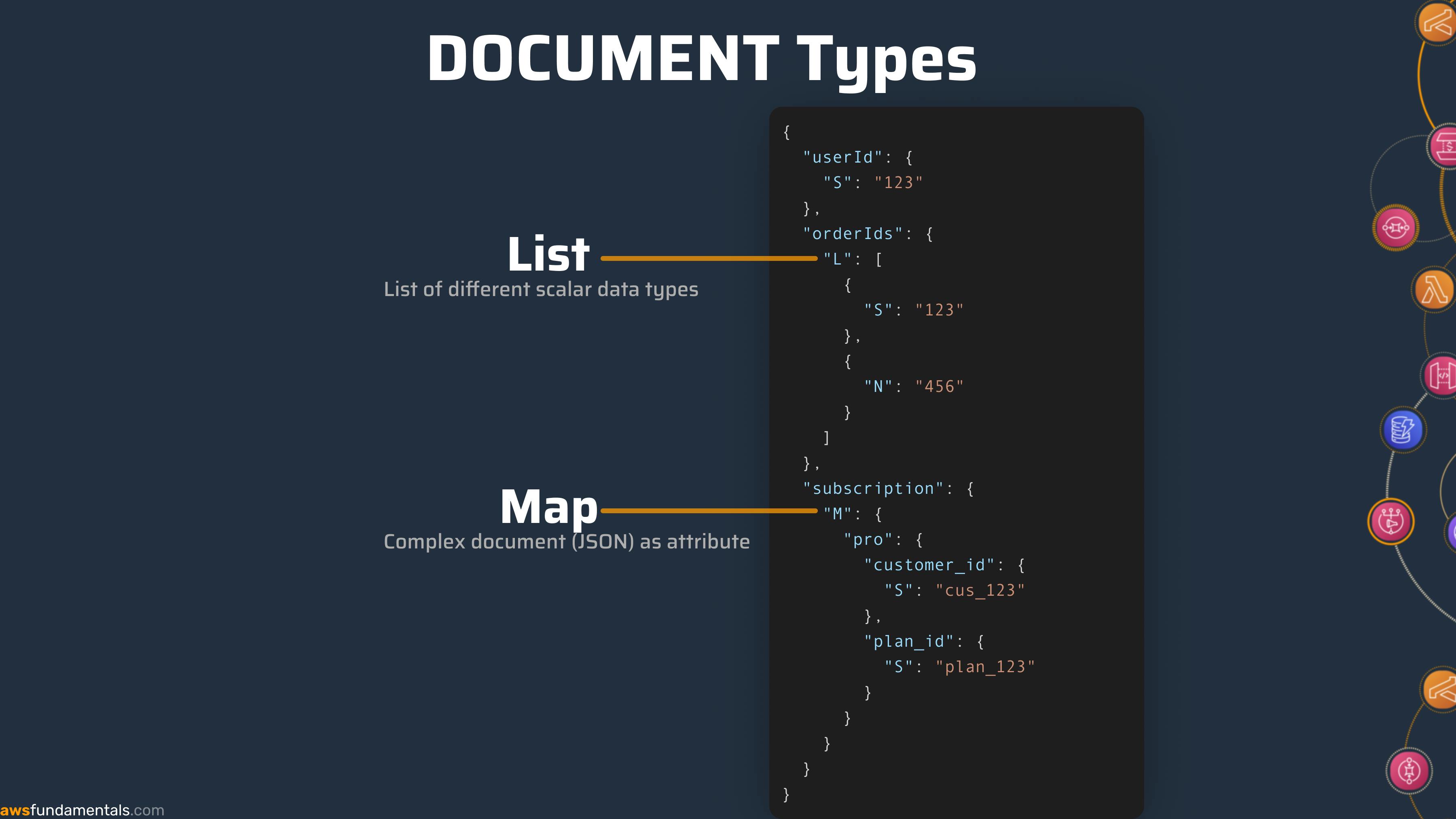
Document datatypes have a bit more of a complex structure. They can either be a list (array) or a map (JSON document).
| Data type | DynamoDB Representation |
| List | L |
| Map | M |
A list is a simple array of similar or different scalar types. For example, for our user example, we could have a list of all orderIds. This list can contain numbers but it can also contain strings.
DynamoDB JSON
{
"userId": {
"S": "123"
},
"createdAt": {
"S": "2022-08-20"
},
"firstname": {
"S": "Sandro"
},
"lastname": {
"S": "Volpicella"
},
"orderIds": {
"L": [
{
"S": "123"
},
{
"N": "456"
}
]
}
}
Normalized JSON
{
"userId": "123",
"createdAt": "2022-08-20",
"firstname": "Sandro",
"lastname": "Volpicella",
"orderIds": ["123", "456", "789"]
}
Each item in a list can have a different scalar type. So the list could also look like that: [123, "ORDER", NULL]
Map - This is again a JSON document as an attribute. A common example is to have a subscription object in your user model.
DynamoDB JSON
{
"userId": {
"S": "123"
},
"createdAt": {
"S": "2022-08-20"
},
"firstname": {
"S": "Sandro"
},
"lastname": {
"S": "Volpicella"
},
"subscription": {
"M": {
"customer_id": {
"S": "cus_123"
},
"plan_id": {
"S": "plan_123"
}
}
}
}
Normalized JSON
{
"userId": "123",
"createdAt": "2022-08-20",
"firstname": "Sandro",
"lastname": "Volpicella",
"subscription": {
"customer_id": "cus_123",
"plan_id": "plan_123"
}
}
You can see that the user now has an attribute subscription with a simple object customer_id and plan_id. This makes DynamoDB very powerful.
Set Types
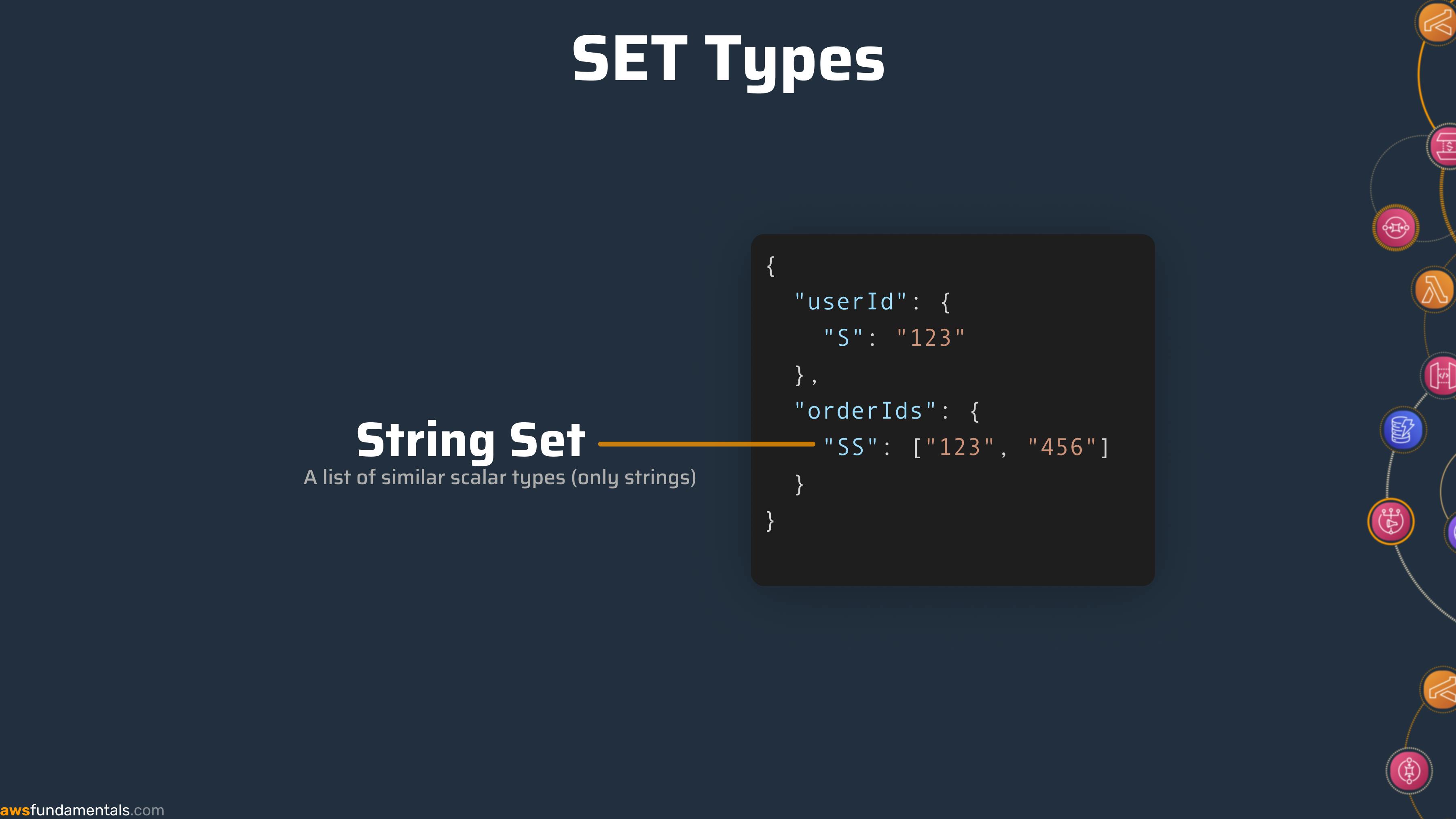
Set datatypes represent a list of the same scalar value. There are three different set types out there.
| Data type | DynamoDB Representation |
| String Set | SS |
| Number Set | NS |
| Binary Set | BS |
While a normal list can have different types mixed (like number, string, and NULL). A Set type can only have one type. If we take our orderIds as an example, this would be a String Set
DynamoDB JSON
{
"userId": {
"S": "123"
},
"createdAt": {
"S": "2022-08-20"
},
"firstname": {
"S": "Sandro"
},
"lastname": {
"S": "Volpicella"
},
"orderIds": {
"SS": [ "123", "456"]
}
}
Normalized JSON
{
"userId": "123",
"createdAt": "2022-08-20",
"firstname": "Sandro",
"lastname": "Volpicella",
"orderIds": ["123", "456"]
}
Final Words
This is all about DynamoDB Data Types. DynamoDB is a really powerful service and makes developing applications on AWS a blast!

