Introduction
Amazon EventBridge is one of the newer services in AWS which launched back in 2019. Before the launch, the service existed with fewer features as CloudWatch Events.
EventBridge makes it easier to build Event-Driven architectures by integrating AWS services without code.
This article will go into the various functionalities EventBridge offers and explains the pricing.
EventBridge Pricing
The pricing in EventBridge depends on quite a few factors and their products. This chapter will give you a brief introduction to each service, explain the pricing structure, and give an example for each section.
The number one thing to keep in mind is that EventBridge is a serverless service. That means it is completely usage-based. There are no upfront or minimum costs. All costs depend on how many events you send or schedule.
Each product of EventBridge (EventBridge Events, Pipes, Scheduler, ...) have kind of their own pricing.
Always use the official AWS Pricing Calculator to get a clue about the pricing of different AWS services. For EventBridge the calculator looks slightly complicated with tons of different options:
Payload
EventBridge
API Destinations
Event Replay
EventBridge Pipes
Schema Discovery
EventBridge Scheduler
Let's go through them and see them in detail.
EventBridge
The first category we look at is EventBridge. EventBridge is all about sending events to an event bus**.** In EventBridge you mainly use three different components:
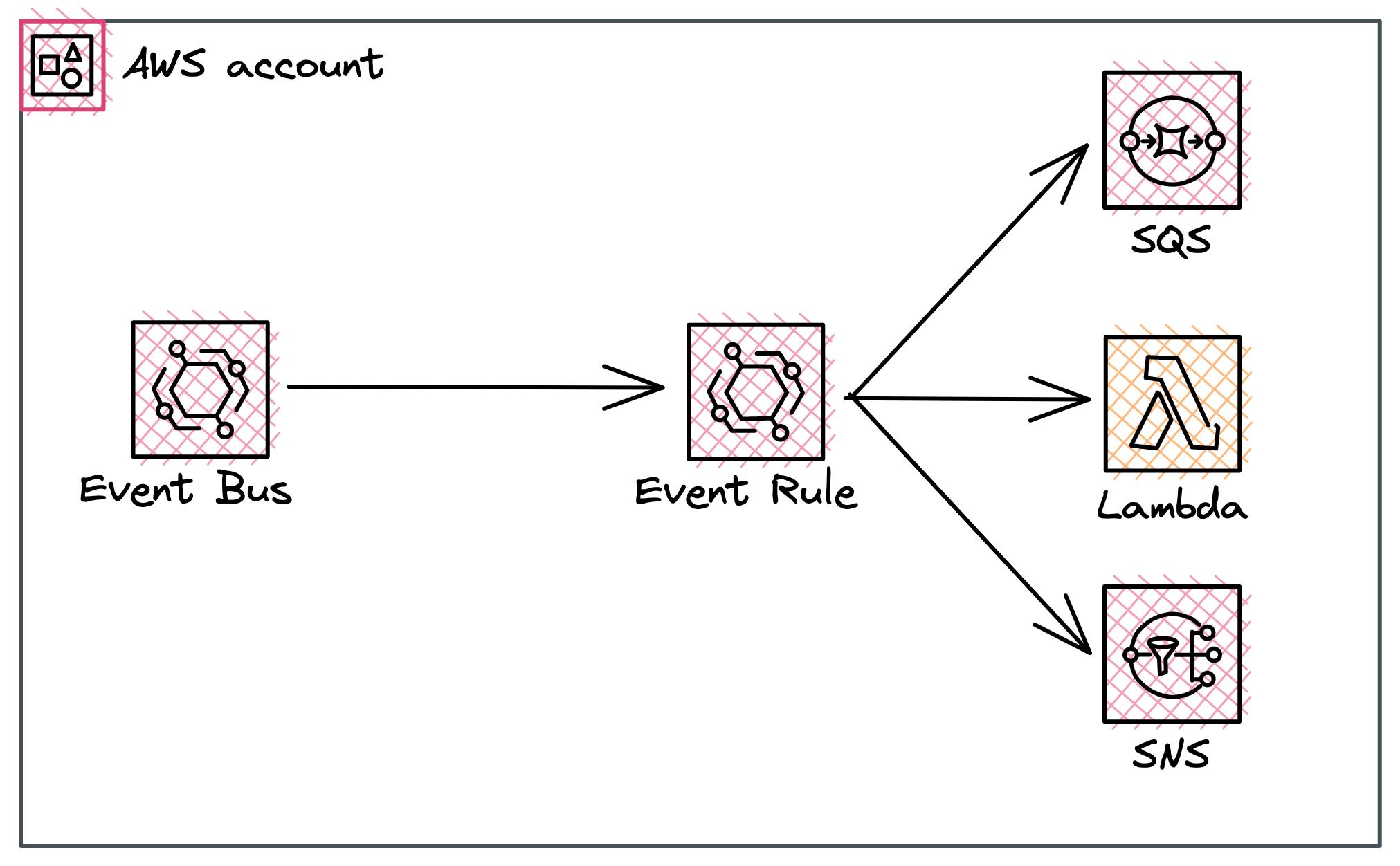
Event Bus: Receiver of all Events
Event Rule: How will events be routed?
Target: The receive of events
The EventBridge section refers to your normal usage of EventBridge. I call it normal because it is the core usage of EventBridge. Sending events to an Event Bus and forwarding them based on rules.
EventBridge has four different kinds of events:
Internal AWS Events -*free*
Custom Events-*not free*
Partner Events-*not free*
Cross-account events-*not free*
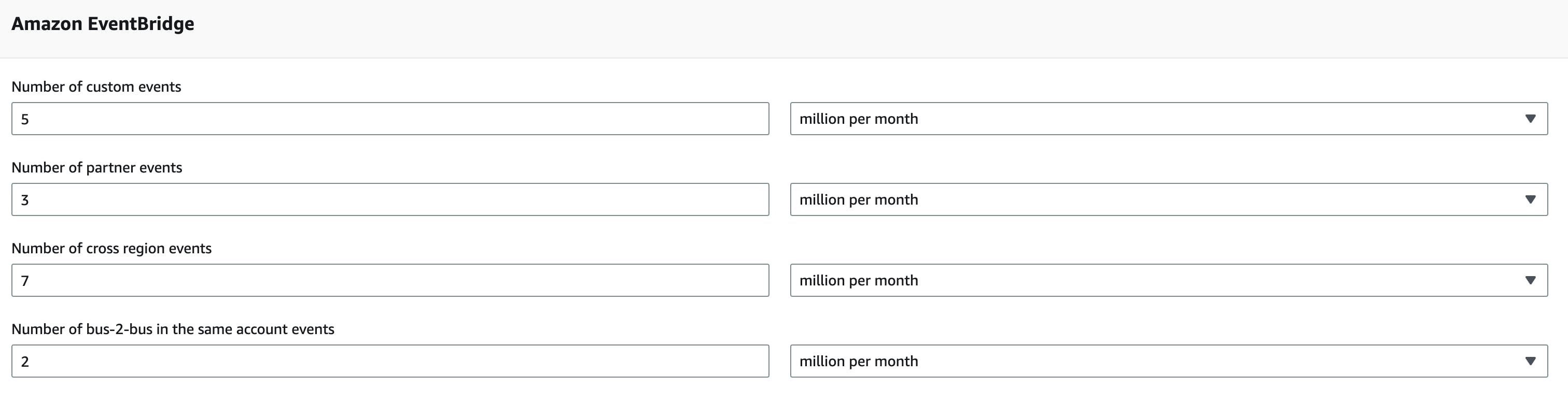
Custom-, partner-, and cross-account-events cost $1.00 per 1 million events published. But there is one other factor to consider: Payload
Payload
The payload refers to the size of one event. One event can't have more than 64 KB. If the event is bigger it counts as multiple events in terms of billing. That means if you send an Event with 128 KB they are counted as 2 events. This can get quite confusing when looking at your bill.
Example Pricing:
Your applications send the following events with each 60 KB payload per month:
5 million custom events
3 million partner events (e.g. MongoDB)
7 million cross-region events
2 million bus-2-bus events
Since the pricing is exactly the same you can simply sum up the events and multiply it by $1.00 per million events:
17∗1.00=$17.00 per month
EventBridge Pipes
EventBridge Pipes were announced together with the EventBridge Scheduler in 2022. It allows you to connect your data sources and transform data before sending it to your target. All of that without custom code in between.
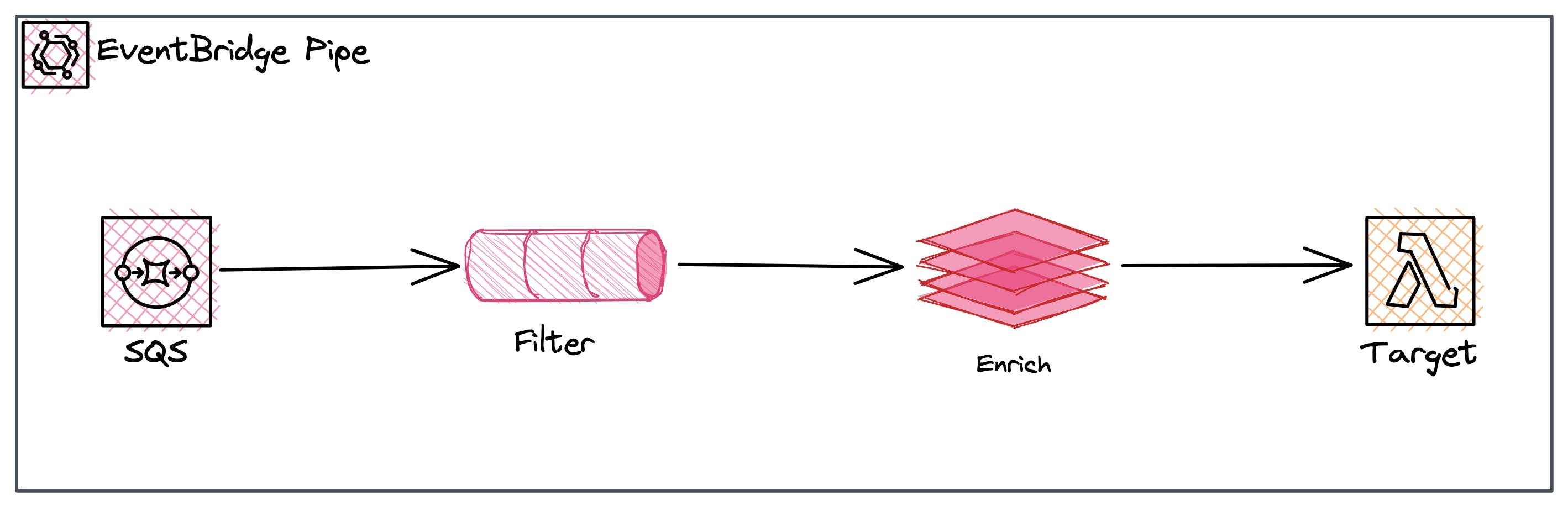
EventBridge Pipes Pricing is calculated by the requests after filtering. It costs $0.40 per million requests that enter a pipe after the filter step.
The same payload size applies to this pricing. 64 KB counts as one request. Anything that is bigger is calculated as another request.
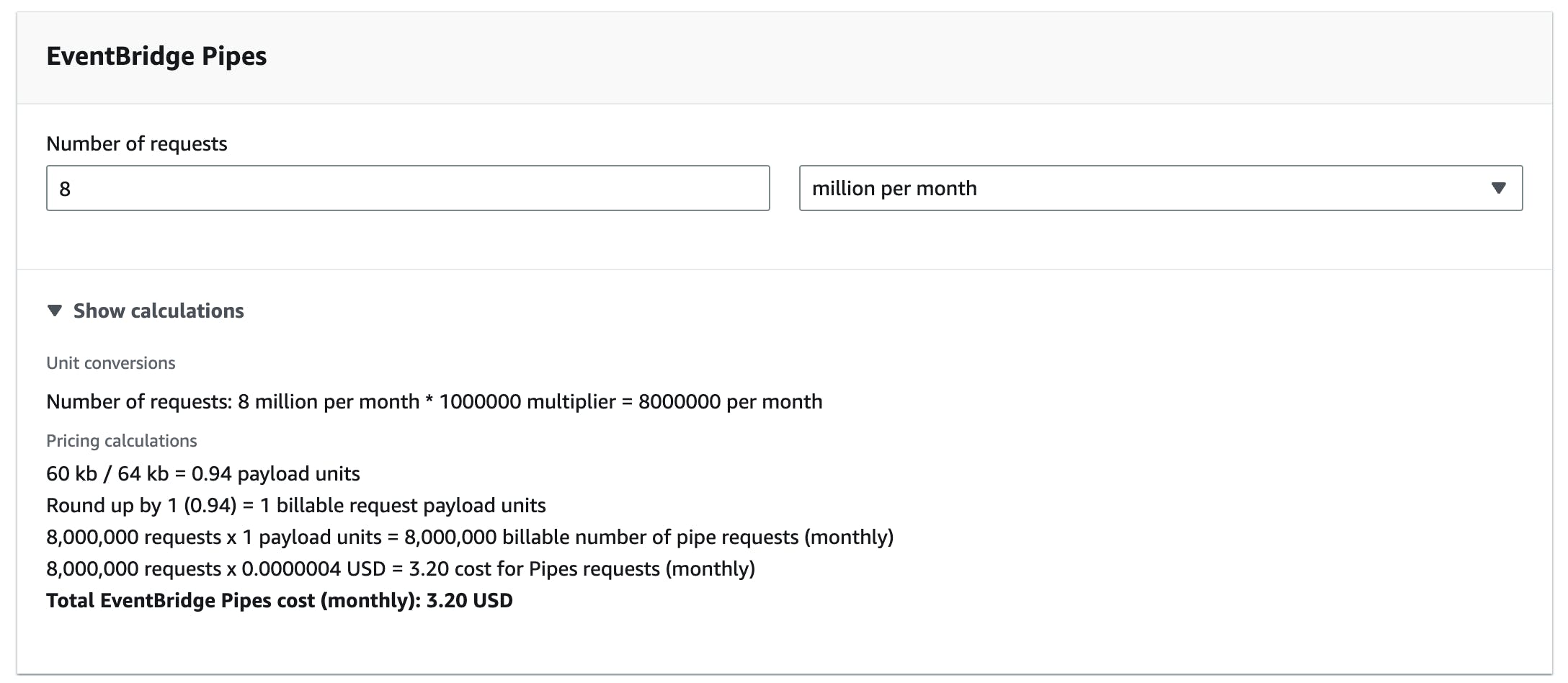
Pricing Example
If you have 8 million events per month. With a payload size of 60 KB (equals 1 event) you have 8 million billable events.
8 million∗$0.40=$3.20
EventBridge Scheduler
In 2022, the EventBridge Scheduler was introduced, allowing you to create both one-time and recurring schedules. You have the option to run a CRON job or set a fixed rate for your schedule to execute.
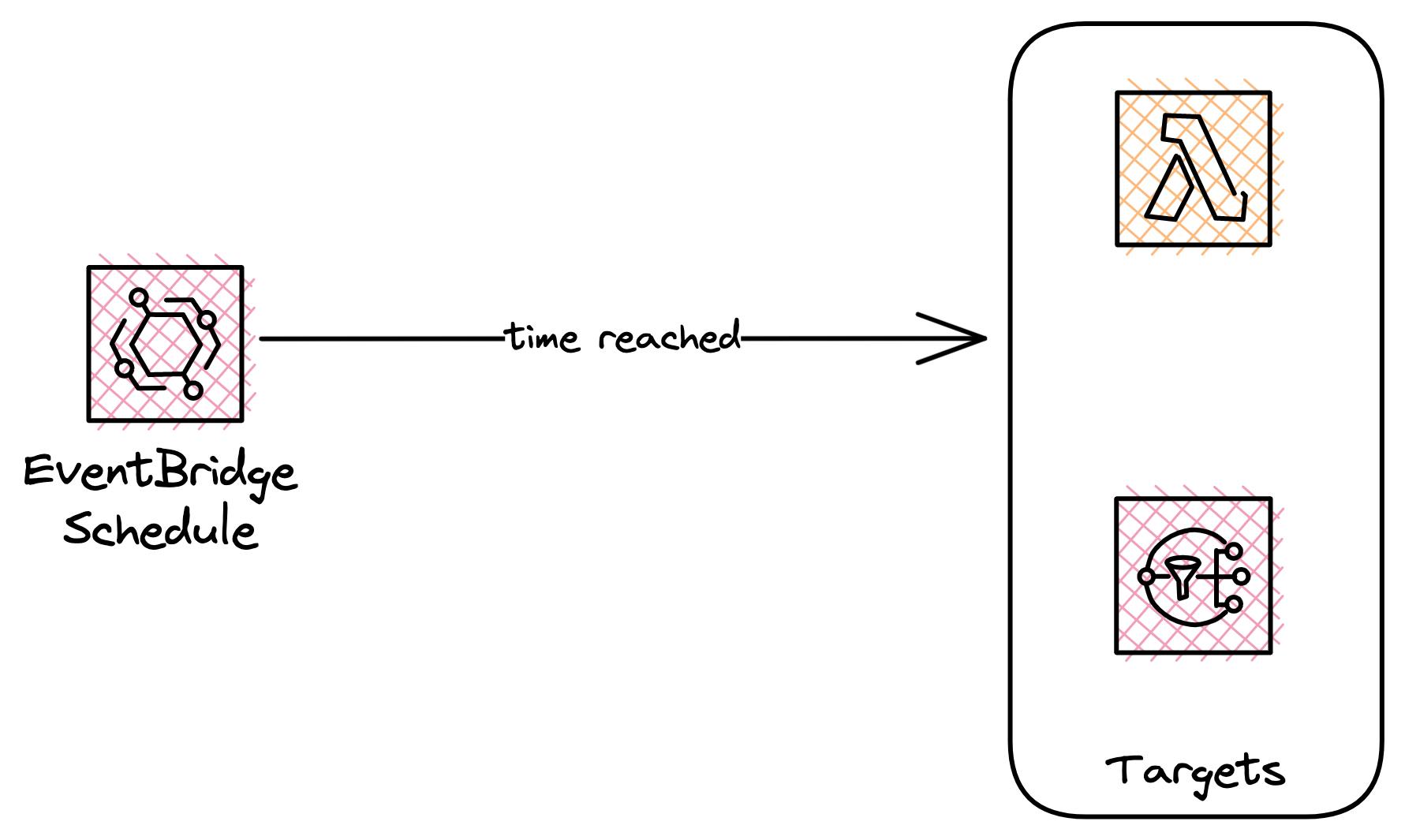
The scheduler then triggers a target (akin to standard EventBridge events) once the specified time is reached.
The EventBridge Scheduler pricing is determined exclusively by the monthly request count.
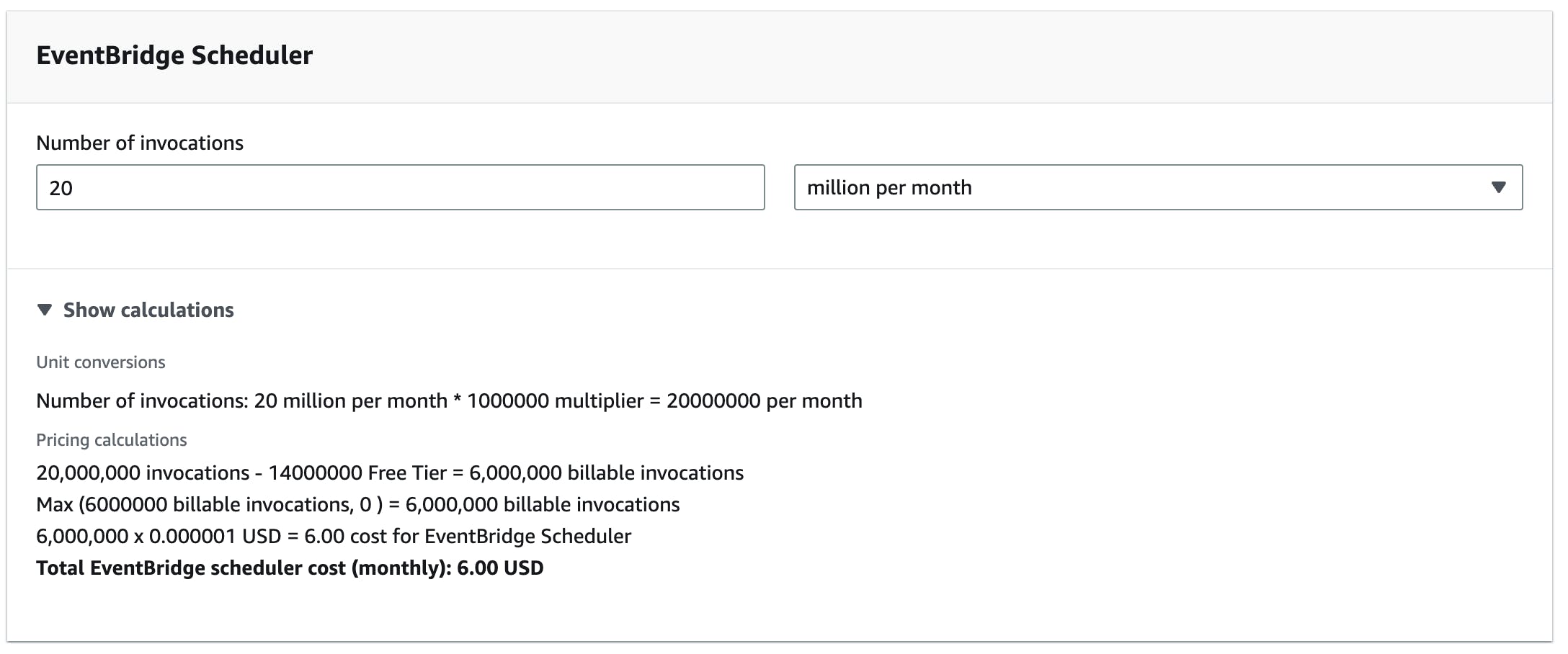
Free Tier: 14,000,000 invocations per month are free! This is a lot.
For one-time schedules, you pay $1.00 per 1 million scheduler invocations per month.
Pricing Example:
If you have 20 million invocations per month defined by your scheduler and you are still in the free tier period (first 12 months). You will have 6 million billable invocations. These invocations cost you $1.00 per 1 million invocations:
6 million∗$1.00=$6.00
API Destinations
The next category is API destinations. You can directly connect EventBridge with external API destinations. This is great because you don't need a Lambda function in between for sending data to an external API.
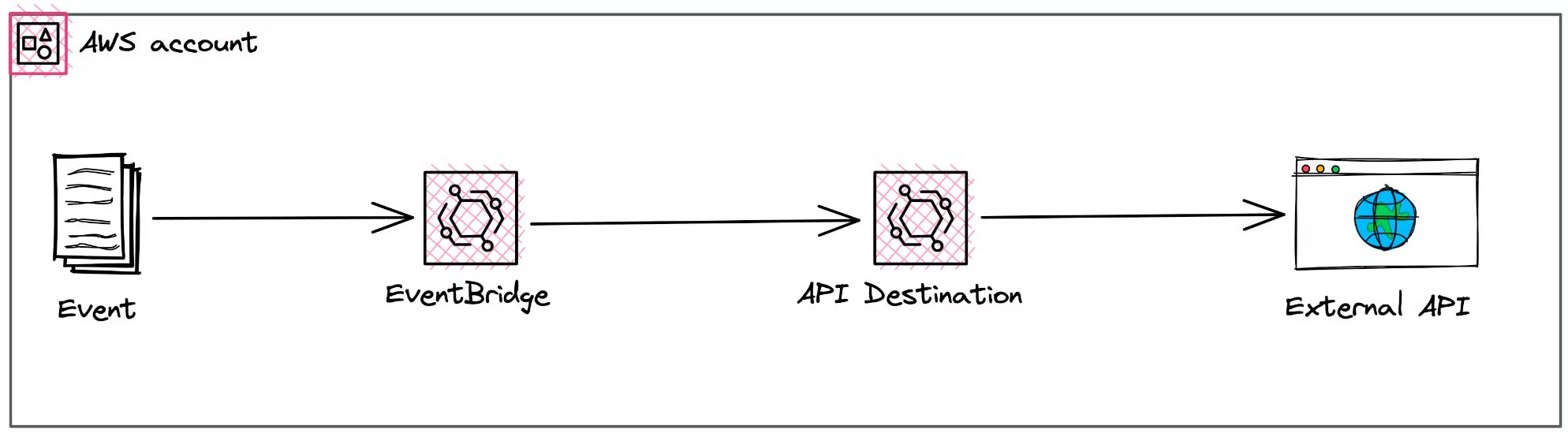
API Destinations are also billed by the number of invocations.
They cost $0.20 per million invocations. In API Destinations the payload of 64 KB is again important to consider.
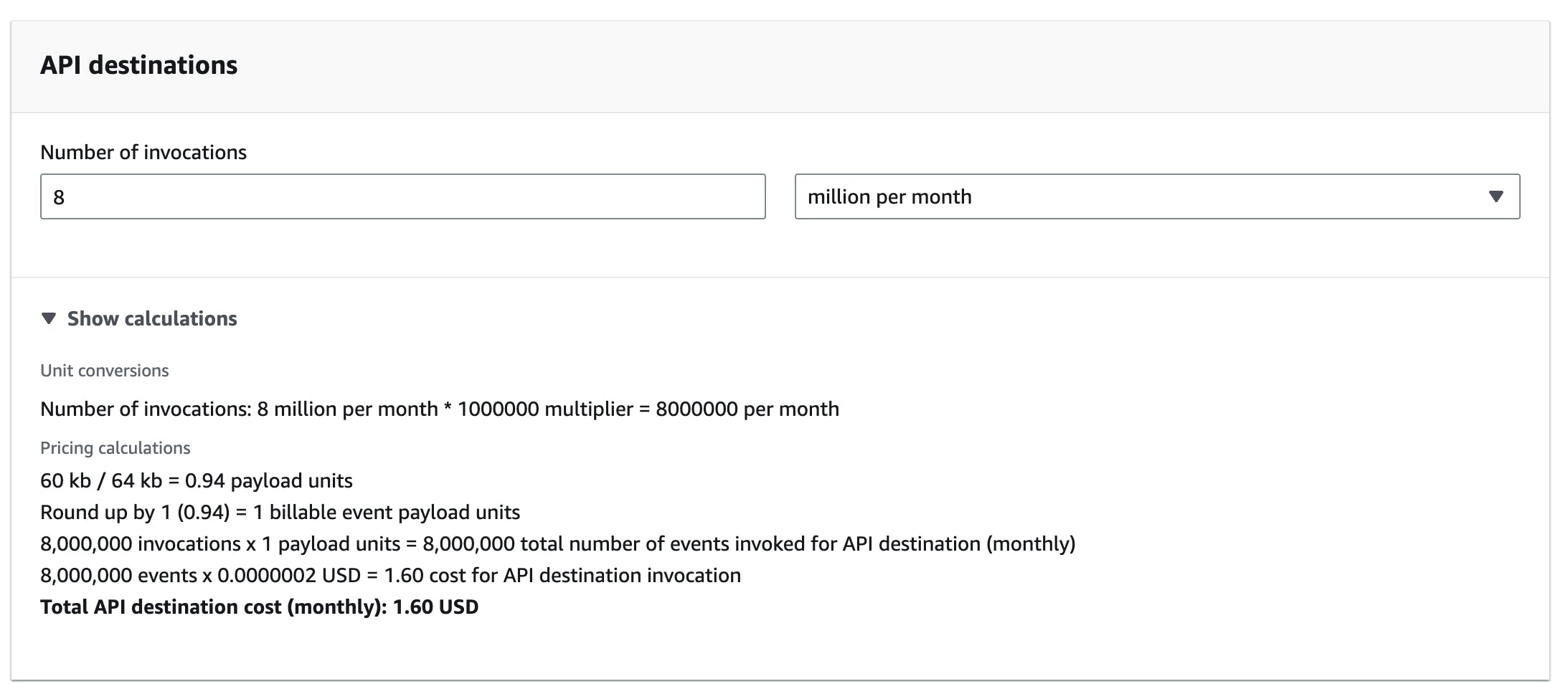
Assuming our 60 KB payload again and 8 million invocations per month we would pay the following:
8 million∗$0.20=$1.60
Event Replay
Introduction
One of the really cool features of EventBridge is the ability to Archive and replay your events. That means EventBridge saves all of your incoming events internally for a defined time (e.g. 14 days). You have the ability to replay all events to certain rules or event buses for example, in case you've introduced a bug. This is a really powerful feature.
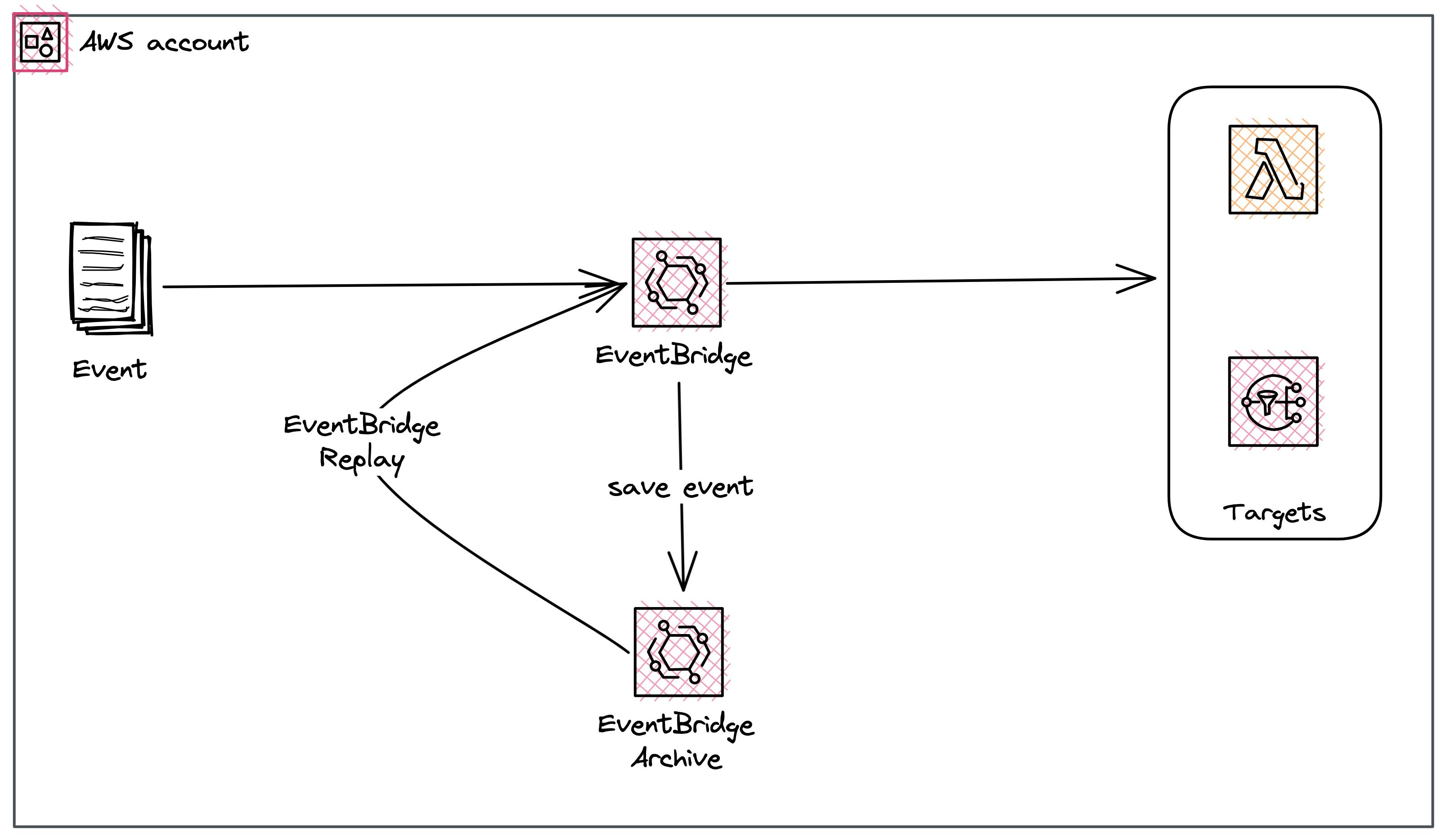
Pricing
The pricing of event replay has several factors
Archive processing - The fee to store your events is $0.10 per GB
Storage costs - The cost to store your data is $0.023 per GB
Replaying events - The cost to replay your data is $1.00 per million
Here is an example of the pricing calculator:
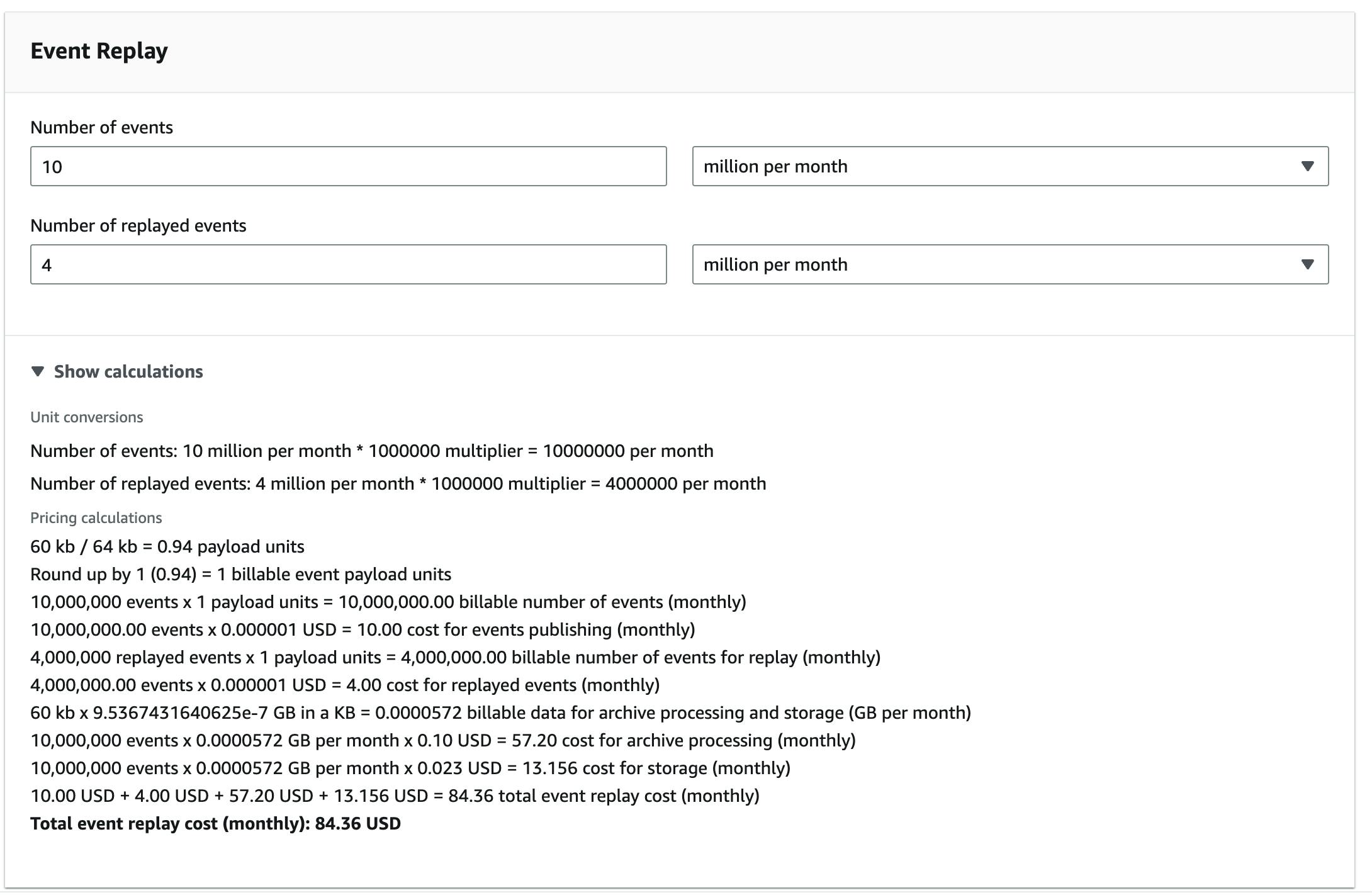
Pricing Example
Let's assume your application publishes 10 million events per month. We ignore the other fees that are applicable for publishing these events and focus only on the Event Replay category.
The following costs would appear:
Archive Processing: 10 million events ∗ 0.0000572 GB ∗ $0.10 = $57.20
Storage Fee: 10 million events ∗ 0.0000572 GB ∗ $0.023 = $13.16
Event Replay: 4 million events ∗ $1.00 = $4.00
Sum: $57.20 + $13.16 + $4.00 = $74.36
Conclusion
In conclusion, AWS EventBridge is a powerful serverless service that offers many functionalities for building event-driven architectures without code.
The pricing structure can be complex, but understanding the different components and their costs will help with cost management. It's important to keep in mind that all costs depend on usage, with no upfront or minimum costs.
Overall, EventBridge is a valuable addition to the AWS suite of services for those looking to build event-driven architectures.
Are you interested in more?
Head over to our bi-weekly newsletter or check out the following blog posts

